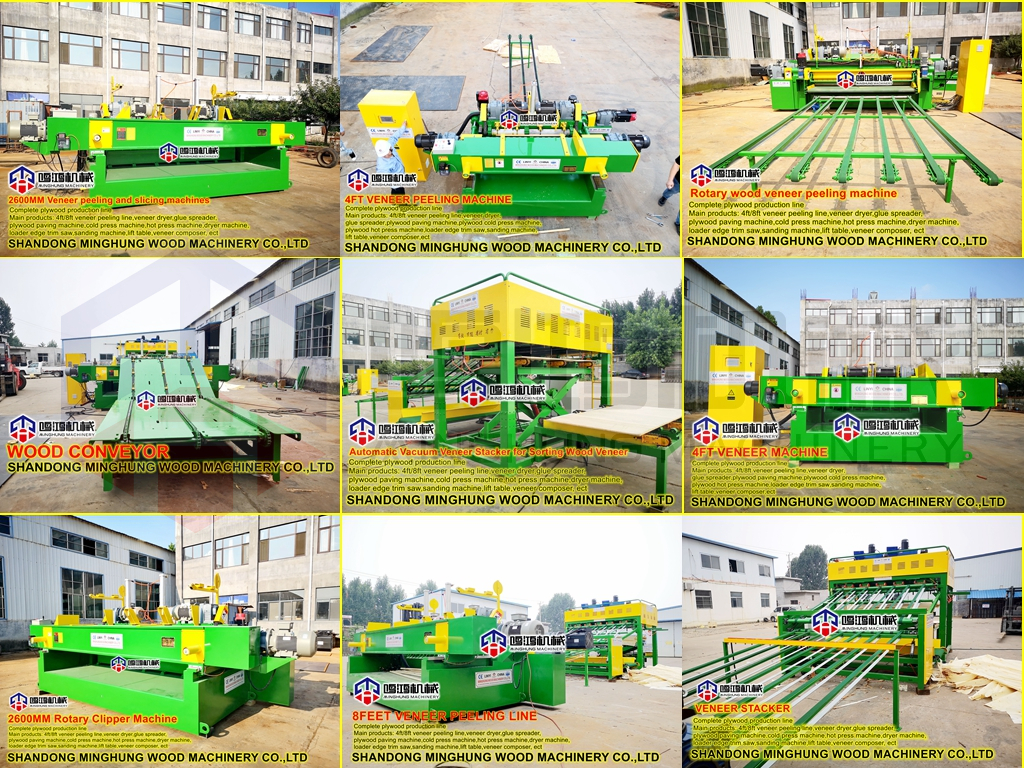
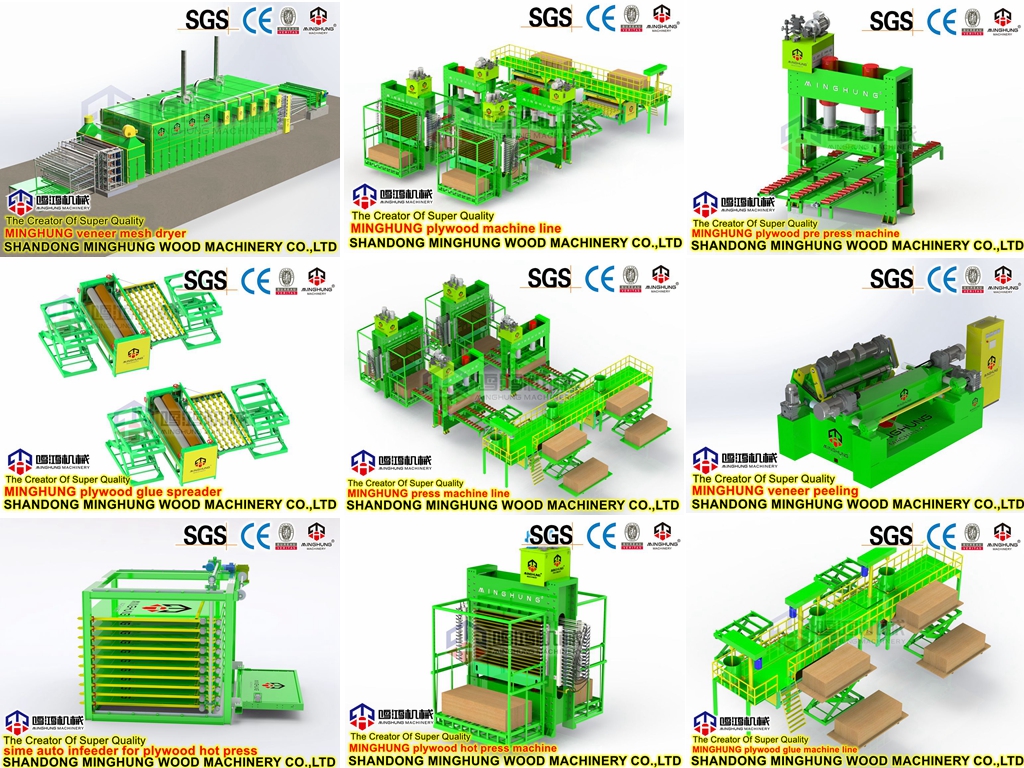
Annual output of 50,000 cubic meters
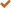 | 1. Scale and Level |
A plywood production line with an annual capacity of 50,000 cubic meters is classified as a medium to upper-medium scale operation, representing an excellent balance between cost-effectiveness and market demand.
Industry Positioning: Significantly larger than small family-run workshops (annual output of a few thousand to 10,000 m³) but smaller than large, fully automated giant factories (annual capacity >100,000 m³). It is a highly practical and competitive scale.
Investment Characteristics: Requires substantial initial investment (equipment, factory, land), but compared to super-large production lines, the entry barrier is lower, and the return on investment is more manageable.
Production Characteristics:
Daily Output: Calculated based on 300 working days per year, the daily output is approximately 167 m³.
Organization: Typically adopts a semi-automated model of "automation in key processes (peeling, drying, hot pressing) + manual assistance (layup, patching, loading/unloading)", which is the mainstream choice in current domestic and international markets.
Product Adaptability: The scale is sufficient to produce various specifications and thicknesses (e.g., common 4-18mm thicknesses), allowing flexibility to respond to market changes. It can steadily supply construction template manufacturers and also produce ordinary plywood for furniture and decoration.
Market Positioning: This capacity is sufficient to become a key supplier in a region, capable of undertaking medium-sized project contracts and export orders while supplying local wholesalers.
 | 2. Raw Material Consumption |
Raw material consumption is the core of cost calculation and depends primarily on the log species and veneer recovery rate.
Core Raw Material: Logs (Poplar, Eucalyptus, Birch, Okoume, etc.)
Consumption Estimate:
Comprehensive Yield Rate: The process from log to finished plywood involves multiple stages of loss (debarking, peeling, drying, trimming, sanding). The comprehensive yield rate is usually between 50% - 60%. We will use a median value of 55% for calculation.To maintain an annual output of 50,000 m³ of finished product, approximately 90,000 - 100,000 m³ (solid volume) of logs are consumed annually. This necessitates a very stable and reliable log supply source.
 | 3. Radiation Range |
The radiation range of this production line is primarily constrained by logistics costs and market competition patterns.
3.1 Raw Material Procurement Radius:
Ideal Range: Within 200-300 km. Logs are bulky and heavy, making long-distance transportation extremely costly and a significant profit drain. The factory must be located near the raw material source or a distribution hub.
Maximum Range: If certain precious wood species are not available locally, sourcing from farther away might be necessary, but this would constitute a very small portion of the raw materials.
3.2 Product Sales Radius:
Core Market Circle: Within 500-800 km by road transport. This is the area where the product is most price-competitive. Products can be efficiently distributed to major markets within the province and surrounding provinces via truck transport.
National & Export Markets: Products can be sold nationwide and even overseas (e.g., Middle East, Southeast Asia, Europe, America) via rail or sea. However, beyond the core road transport range, the product's price advantage diminishes, and it must compete based on quality, brand, or special specifications. For a 50,000 m³ capacity, export is an important channel for absorbing capacity and improving profits.
Market Layers: Can simultaneously cover local retail, wholesale in surrounding provinces, national project tenders, and foreign trade exports.
Summary: A 50,000 m³ annual production line is a "capital ship" level project. Its success hinges on: Stable and low-cost raw material supply (localization) + Efficient production management + Flexible and diversified market sales strategy (local, national, international).