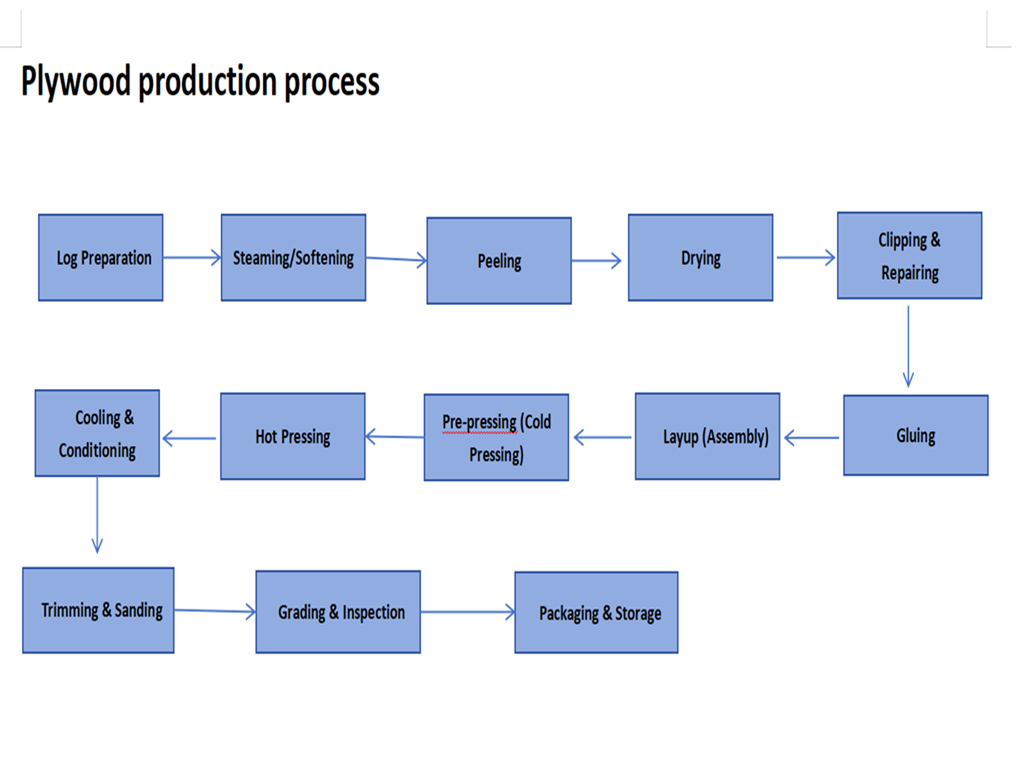
Core Process Flow and Key Equipment
Section 1: Raw Material Processing & Veneer Preparation
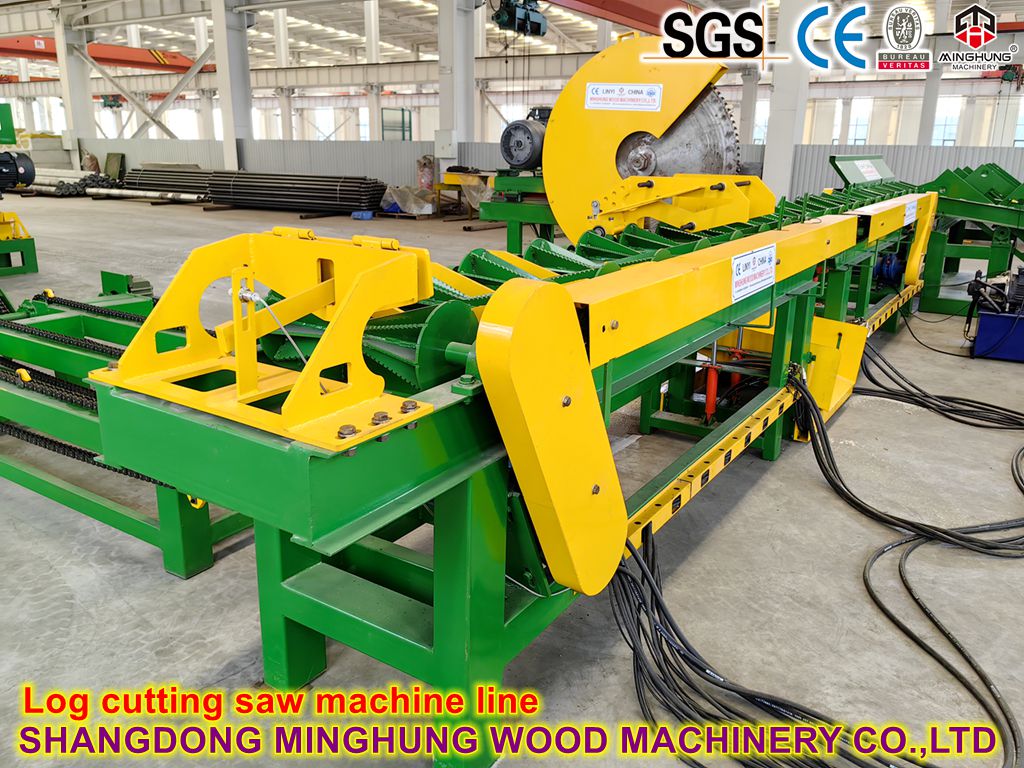
Log Cutting: A Log Debarking Saw cuts long logs into segments of required length.

Debarking: A Drum Debarker or Ring Debarker removes bark to ensure a smooth veneer surface.

Steaming/Cooking: Log segments are softened in a Steaming Pond or Digester to facilitate peeling and reduce splintering.
Peeling: A critical process. Log segments are rotated on a Veneer Lathe and continuously shaved into a continuous veneer ribbon. For mixed hardwoods, the lathe requires robust drive and precise control to handle varying wood hardness.

Veneer Drying & Clipping: Wet veneer is dried to suitable moisture content in a Veneer Dryer (usually roller or mesh belt type). It is then clipped to set dimensions by a Veneer Clipper.

Veneer Sorting & Patching: Dried veneer is graded on a Veneer Sorting Line manually or via vision systems. Defective sections are repaired by Veneer Patching Machines (e.g., for plugging holes, stitching) to improve yield.
Section 2: Gluing & Layup
Gluing: An Glue Spreader (Roller type or 4-Roller type) applies adhesive (e.g., UF, PF resin) evenly onto the veneer surface. Adhesive formulas may need adjustment for mixed hardwoods to ensure good bonding.

Layup/Assembling: According to the target layer count, glued and unglued veneers are laid up cross-wise (with grains perpendicular). An Automatic Layup Machine performs this efficiently and accurately, ensuring symmetrical assembly and preventing warpage.
Section 3: Pressing & Post-Processing
Pre-pressing: Before hot pressing, a Cold Press applies initial pressure to the mat for preliminary shaping, easing transport and preventing misalignment in the hot press.

Hot Pressing: The core forming process. The mat is fed into a Multi-Opening Hot Press , where high temperature (typically 120-180°C) and high pressure (typically 1.0-2.0 MPa) rapidly cure the adhesive, bonding the veneers into a solid panel.

Cooling & Curing: The pressed panels are cooled and set in a Cooler/Stacker, then stored in a Curing Area to allow internal stresses to equilibrate and stabilize performance.

Section 4: Trimming & Sanding
Trimming: A Panel Saw (cross-cut and edge trim) cuts the cooled rough-edged panels into standard-sized finished panels.

Sanding: A Wide Belt Sander (typically a combination of coarse and fine sanding) smoothes the panel surface, ensuring precise, consistent thickness and a smooth finish, providing a perfect substrate for further processing or laminating.

Section 5: Inspection & Packaging
Inspection: Finished panels are inspected for quality, including dimensions, appearance, bond strength, and formaldehyde emissions.
Grading & Packaging: Qualified panels are sorted by grade and packaged by an Automatic Packing Line with filming, strapping, and final packaging.