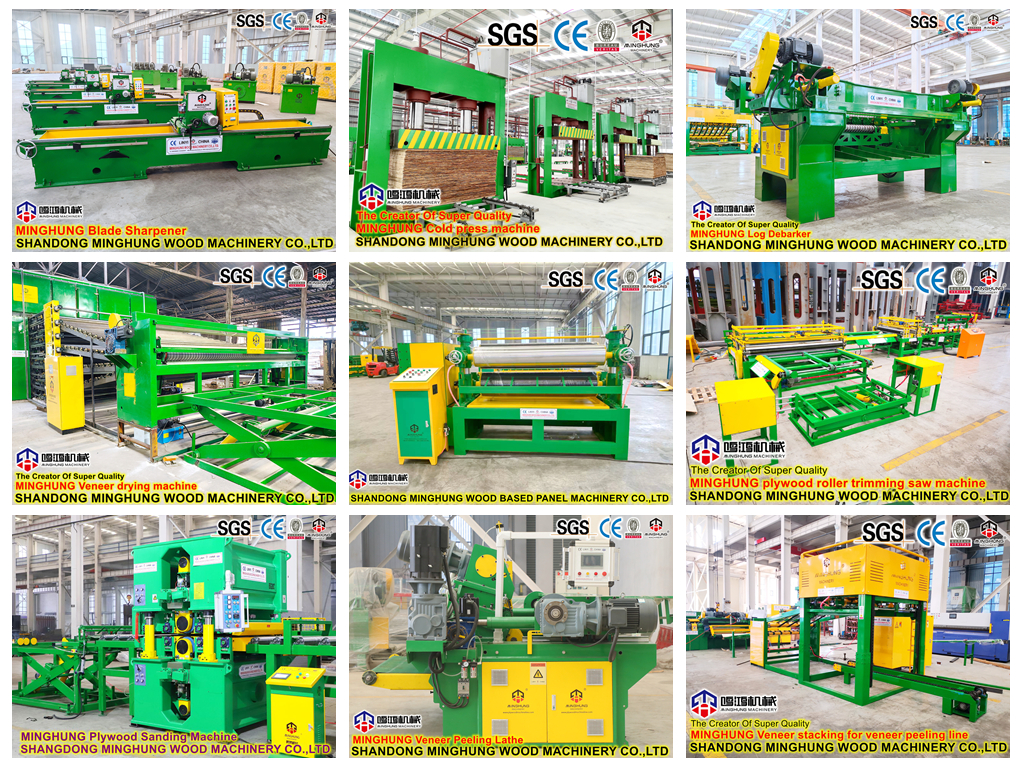
Ⅳ.Machinery and Equipment
To achieve a daily output of 1000 cubic meters (approx. 555 tons, based on 18mm thickness), the production line must be equipped with large-scale, high-efficiency, continuous equipment.
1. Raw Material Handling System
Heavy-duty Chipper: High-power, high-capacity, equipped with heavy-duty flying knives and bed knives for efficient processing of logs, slash, or baled straw.
Drum Screen / Vibrating Screen: For screening chips/flakes to separate qualified raw material.
Magnetic Separator & Washing System: Powerful magnet for removing metal impurities. Wash tank or drum for removing sand and heavy debris.
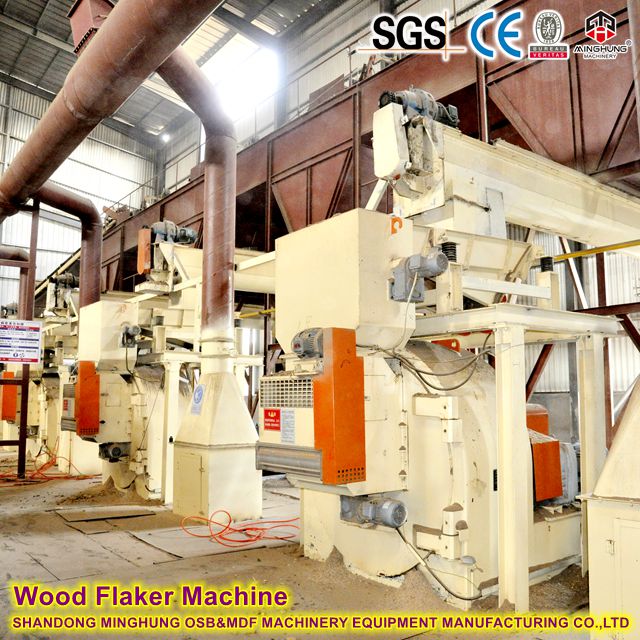

wood flaker

vibrating screen
2. Fiber Preparation System
Pre-steaming Bin: Large vertical bin for sufficient and uniform steam pre-treatment of raw material flakes.
Large-capacity Refiner: The core machine of the line. Must be a high-power (typically several thousand kW), high-capacity (processing tens of tons of oven-dry material per hour) continuous defibrator. Key components include: feed screw, pre-heating digester, screw feeder, main motor, refining plates with refining zone, etc.
Resin Blending System: Includes storage tanks for resin, wax, additives; metering pumps; and high-pressure atomizing nozzles to ensure precise, proportional, and uniform application of chemicals onto the fibers.
Pneumatic Drying System: Large drying pipe, high-efficiency cyclone separators, furnace (thermal energy plant), and exhaust fan. Ensures fibers are dried to the target moisture content (typically 8-12%) in a very short time.

fiber cooking and refining system

glue mixer

fiber drying system
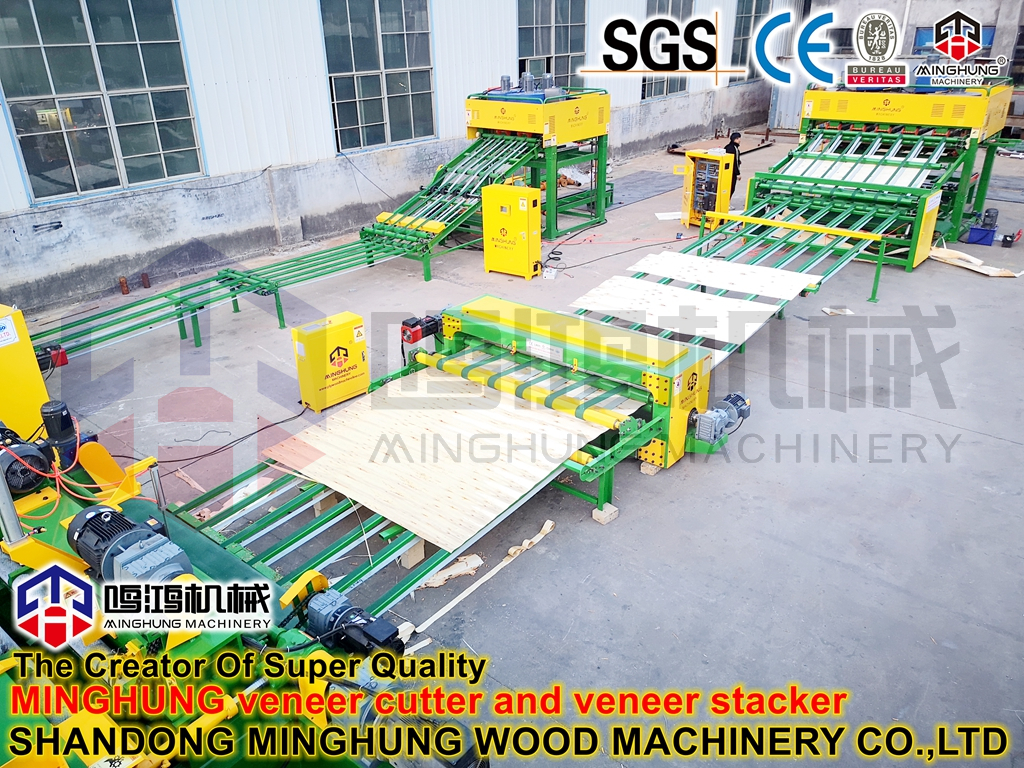
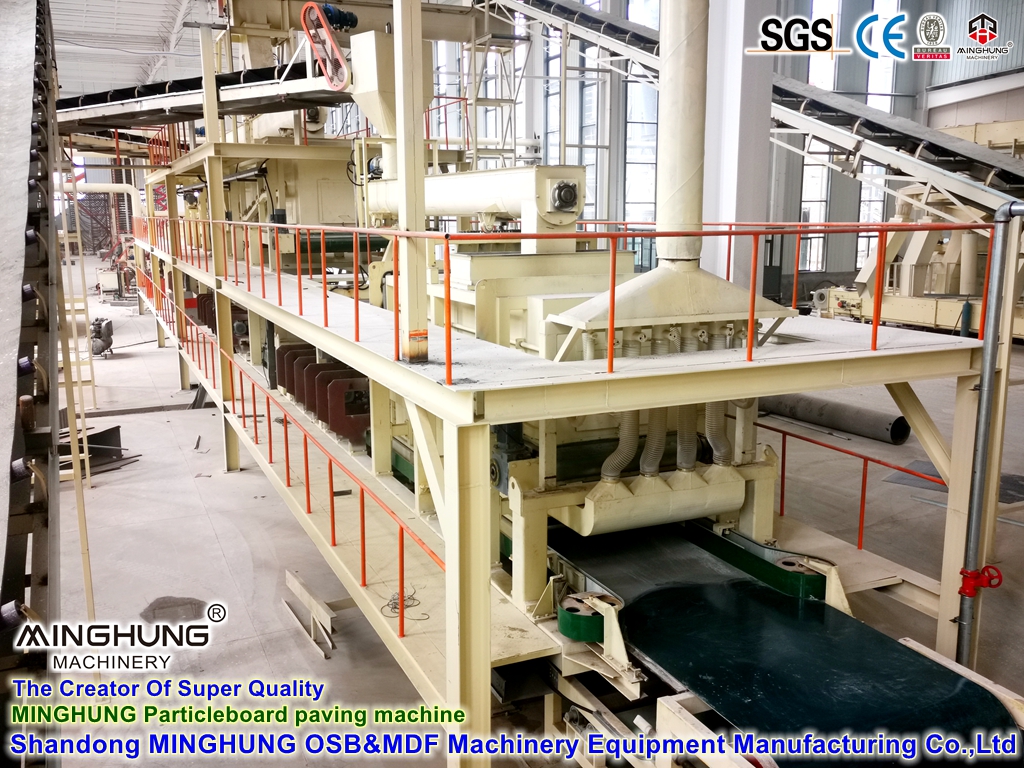
3. Forming and Pre-pressing System
Air-laid Forming Station: A 1000 m³/day line requires a multi-head, scanning-type air forming station. Its core is the forming head and scanning/oscillating mechanism, ensuring absolutely uniform fiber distribution both longitudinally and transversely across the wide (typically over 8 feet) caul screen. This is key to consistent board quality.
Continuous Belt Pre-press: Applies gradual pressure to the fluffy fiber mat via two large pressing steel belts for initial compaction.

mat forming machine

pre press
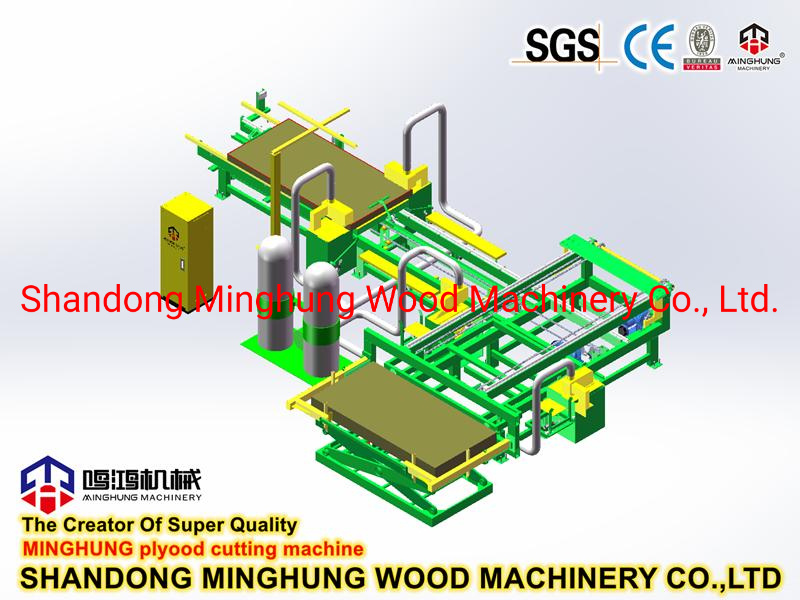
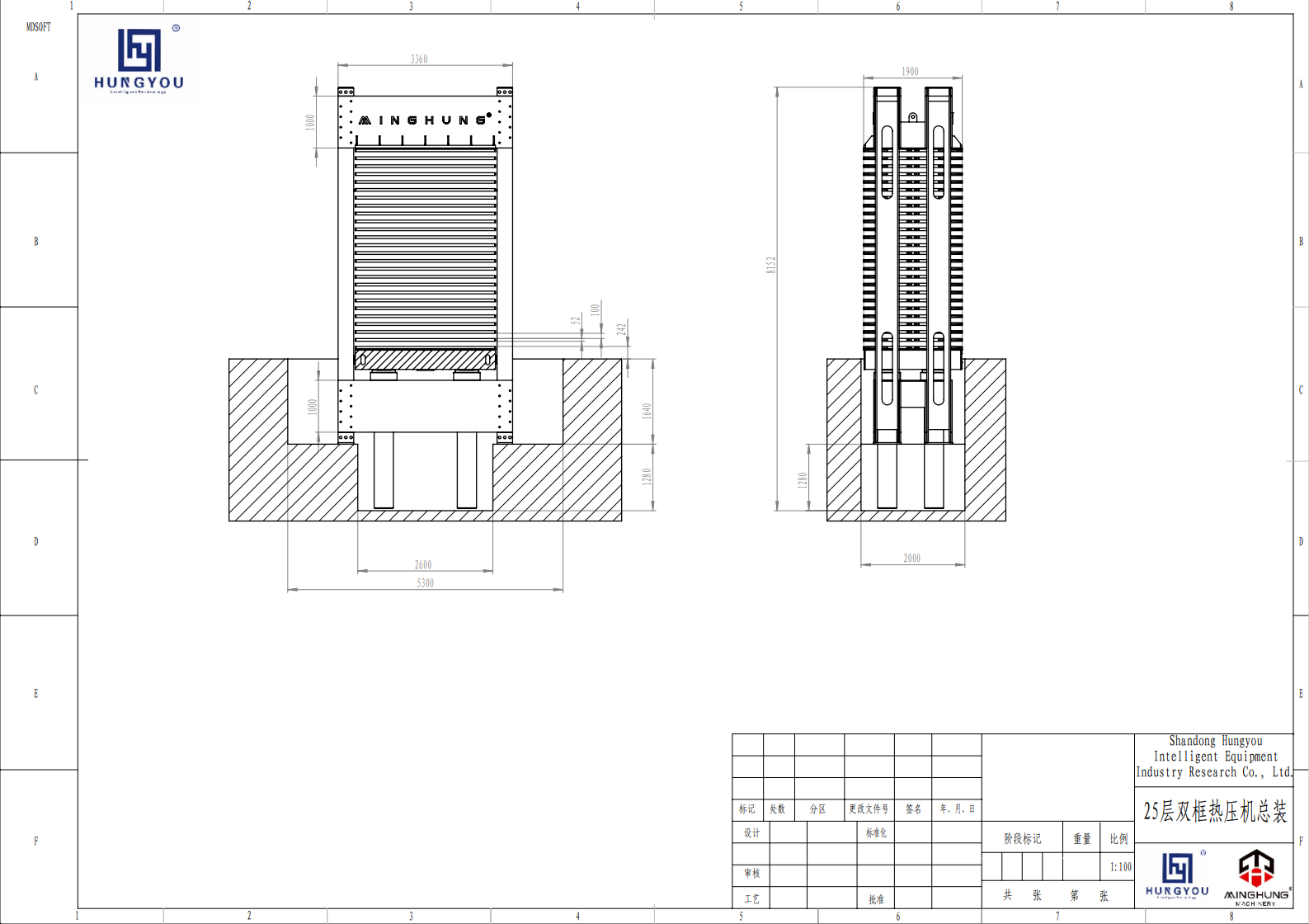
4. Hot Pressing System
Continuous Flat Press: Key equipment for high output. Its working principle: the mat is conveyed between two massive, continuously circulating steel belts (one or both heated) and pressed by a complex array of hydraulic cylinders applying uniform pressure and heat from above. Main components include: press frame, heated steel belt system, hydraulic cylinder array, roller system, drive and control system. It can be dozens of meters long to ensure sufficient press time for complete resin curing.
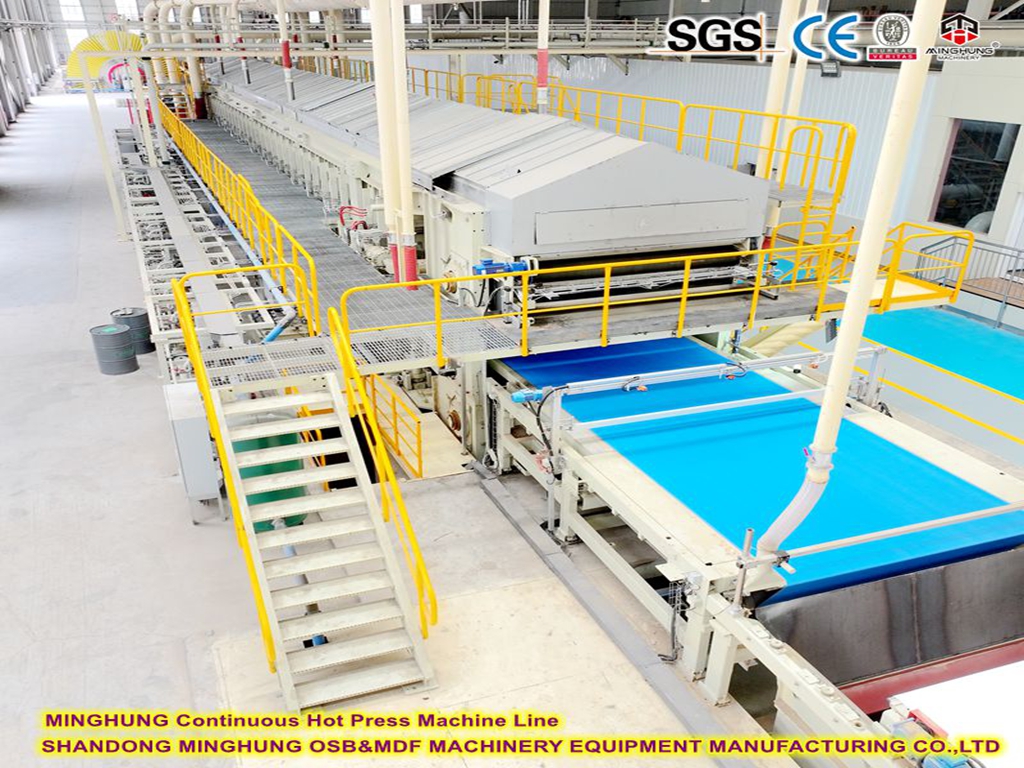

5. Post-processing System
Cooling Star Cooler: Multi-level roller conveyor where boards pass through in an "S" pattern, cooled by fans.
Cross-cut & Edge Trim Saws: High-speed saw units for precise cutting of board length and width.
Multi-head Wide-belt Sander: Typically 6 or more heads (combining coarse and fine sanding), wide sanding belts, high-power motors for high-efficiency, high-precision calibration and sanding of both board surfaces.
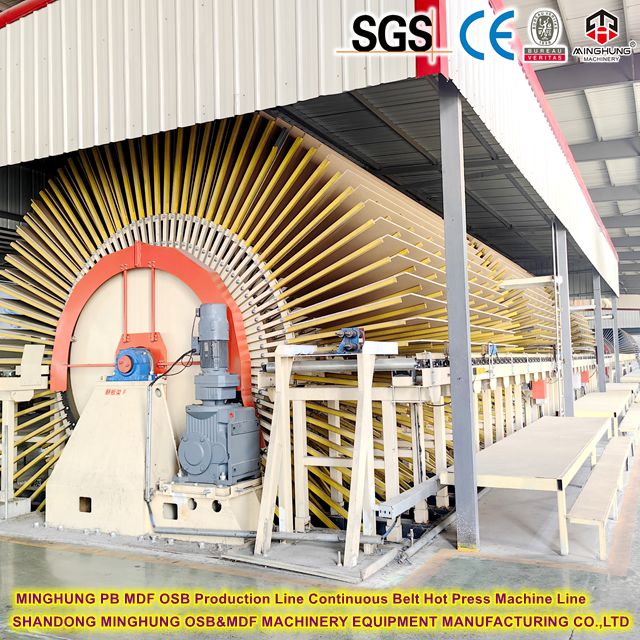

dryer rack
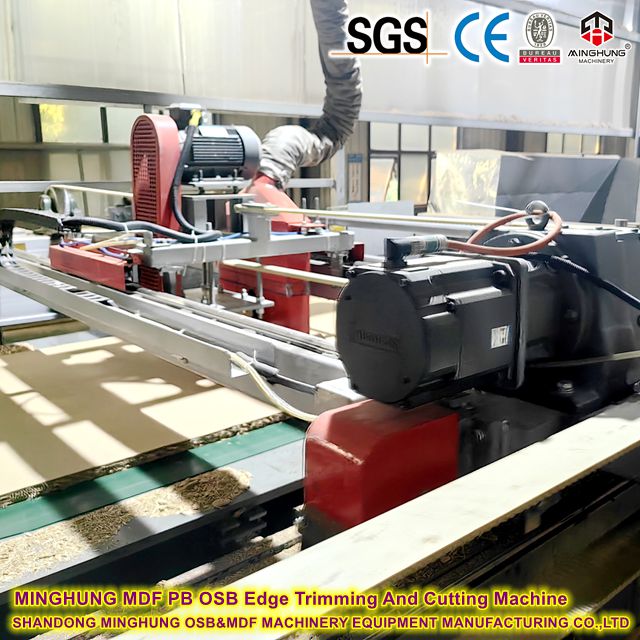

cross-cut saw
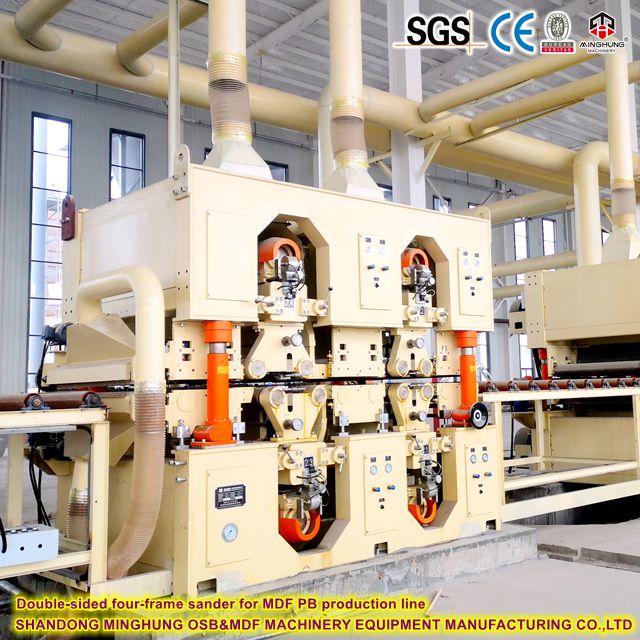

sander
6. Auxiliary Systems
Thermal Energy Plant (TEP): Provides the necessary heat (thermal oil or steam) for core processes (refining, drying, pressing), often fueled by wood waste (bark, sander dust) for energy self-sufficiency.
Central Dust Extraction System: Extensive network of pipes and dust collectors to capture dust from all processes, ensuring a clean and safe production environment.
Automation Control System (DCS/PLC): Distributed Control System monitoring and regulating operating parameters of all equipment, ensuring stable, efficient, and continuous operation of the entire production line.
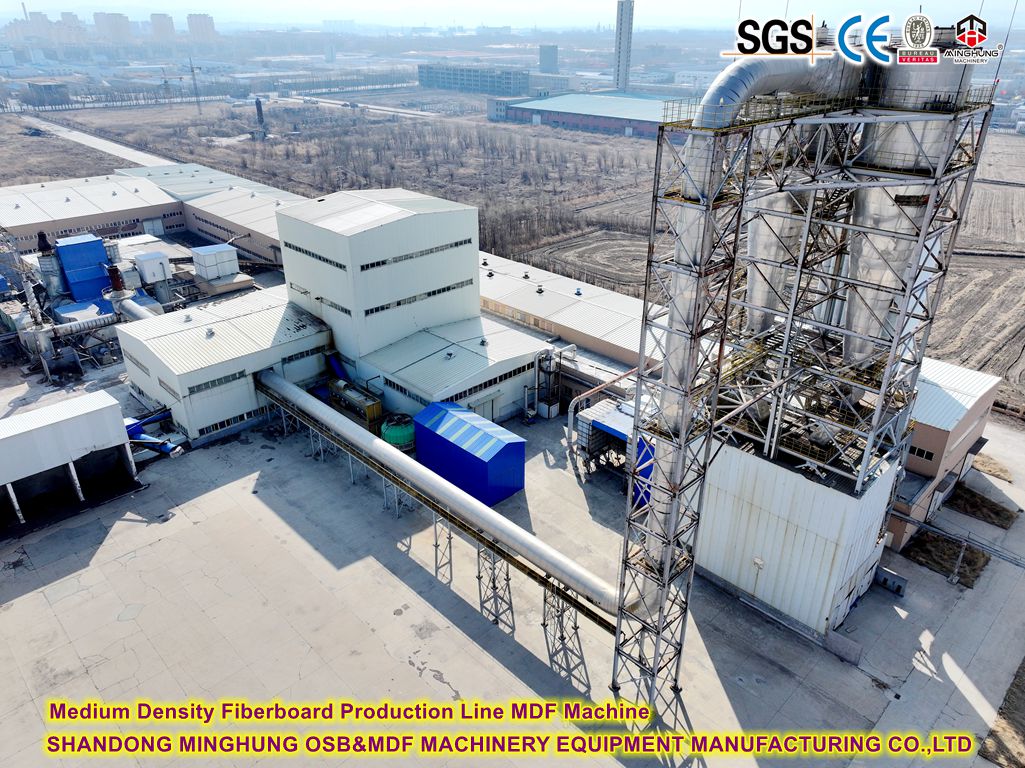

Thermal Energy Center
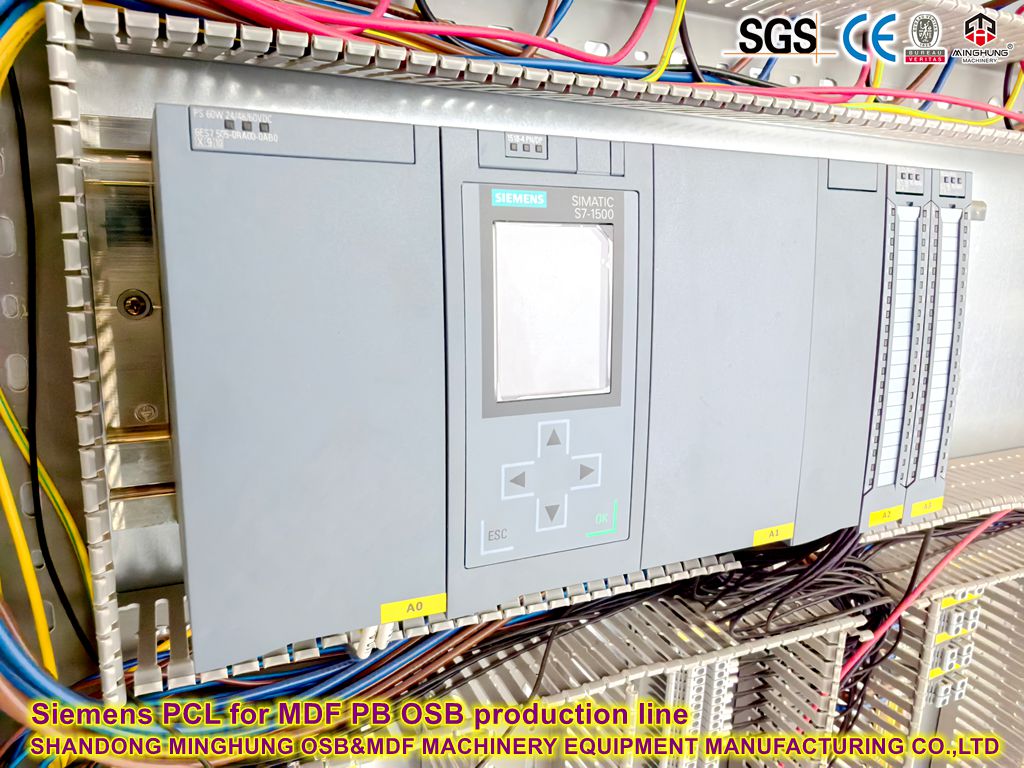

PLC
Ⅴ. Main Application Scenarios
MDF panels made from gramineous crops (e.g., rice straw, wheat straw) are carving out a broad market in numerous fields due to their unique environmental and performance advantages. Their main application scenarios include, but are not limited to, the following areas:
1. Furniture Manufacturing
Panel Furniture: Used for making structural parts of bookcases, wardrobes, TV cabinets, nightstands, as well as non-load-bearing or low-load-bearing components like drawer bottoms, sides, and backs. Their smooth surface is ideal for laminating (with melamine-impregnated paper, veneer), painting, or wrapping.
Office Furniture: Used for office partitions, desk tops (Especially the procurement activities of enterprises that support environmental protection concepts), filing cabinets, etc. Their low formaldehyde emission significantly improves indoor air quality, making them particularly suitable for office environments with limited ventilation.
Custom Furniture & Cabinets: An increasing number of custom furniture brands offer gramineous MDF as an "eco-upgrade" option to consumers, especially for making kitchen cabinet carcasses and doors (substrate). With special treatment, its moisture resistance can also meet the demands of kitchen environments.
2. Interior Decoration & Construction
Door Core Material: This is a very important and high-volume application. As the core filler material for interior doors, molded doors, and fire doors, it is lightweight, offers high flatness and uniform structure, effectively prevents door warping, and provides good sound and thermal insulation.
Wall Panels, Partitions & Ceilings: Used for decorative wall panels, interior partitions, and ceiling materials. Their easy workability allows for creating various shapes, Such as hollowing out, milling patterns, etc., can meet the requirements of various design styles.
Flooring Underlayment: Laid under solid wood or composite flooring as a leveling and cushioning layer. It provides a flat sub-surface, enhances underfoot comfort, and offers some thermal and acoustic insulation.
Baseboards, Mouldings & Picture Frames: Through sawing, milling, and laminating, various specifications and profiles of baseboards, door frames, ceiling mouldings, as well as picture frames and mirror frames can be produced.
3. Packaging Industry
High-end Gift Packaging & Display Stands: Used for high-end packaging inserts, trays for wine, electronics, cosmetics, gifts, and display stands/units for retail stores. Their environmental attribute ("from nature, can return to nature") and customizable appearance align perfectly with green marketing strategies.
Logistics Pallets & Dunnage: In lightweight logistics, it can replace some wood for making disposable or reusable pallets and dunnage, offering lightweight and competitive cost.
4. Other Specialized Applications
Automotive Interiors: Can be used for non-structural interior components like door panel liners, trunk partitions, and seat backboards. Its lightweight characteristic aids in vehicle weight reduction and lower energy consumption.
Household Items & DIY: Used for toys, photo albums, stationery, storage boxes, pet houses, etc. The low-formaldehyde feature is particularly important for home users.
Audio Equipment: Due to its uniform internal structure and stable acoustic properties, some manufacturers use it to make speaker enclosures.
MINGHUNG OSB&MDF Machinery Equipment Manufacture Co., Ltd. Located in Xiaogezhuang Industrial Zone, Yitang Town, Lanshan District, Linyi City.
MINGHUNG Company provides a complete set of process design, electrical design and manufacturing, We can provide one-stop complete factory solutions for wood-based panel customers. MINGHUNG product series include medium density fiberboard (MDF), high density fiberboard (HDF), particle board (PB), oriented strand board (OSB), veneerable super strong particle board (LSB) multi-layer heat press production line, double-sided fixed thickness broadband Sanding machine, gauge saw, mechanical paving machine, air flow paving machine, channel dryer, super screen, post-processing system artificial panel cooling system, turning machine, stacker, storage and transportation trolley. etc. For artificial panel equipment mainly involved in particleboard, medium density fiberboard, oriented strand board, multilayer plywood machinery.
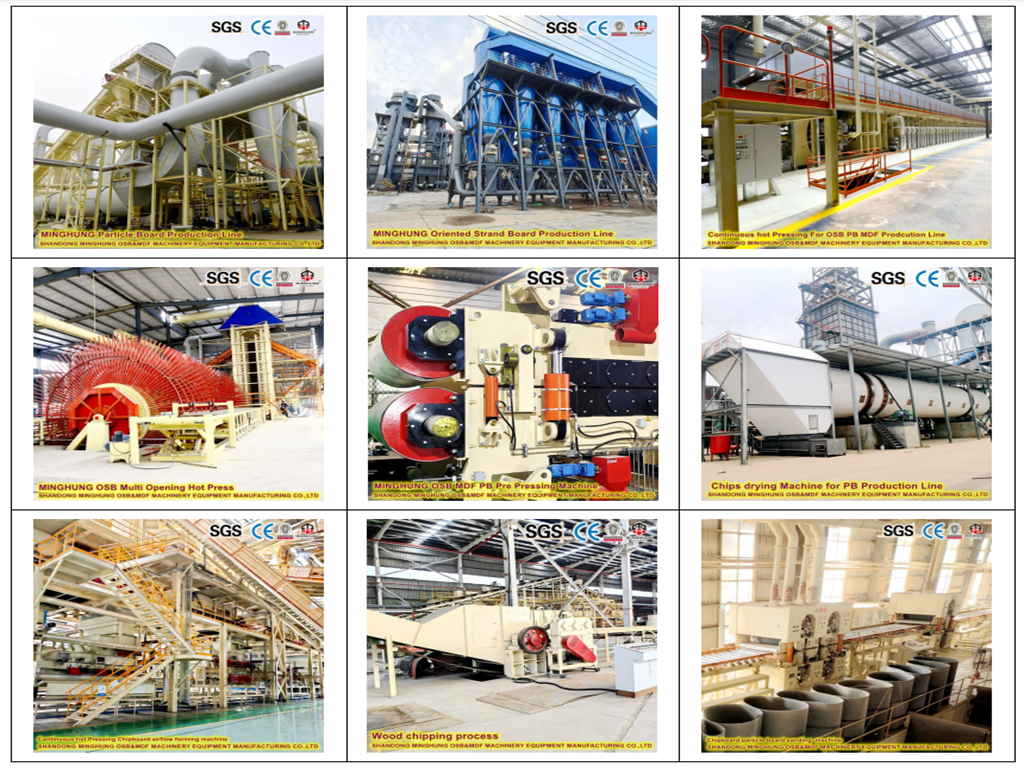
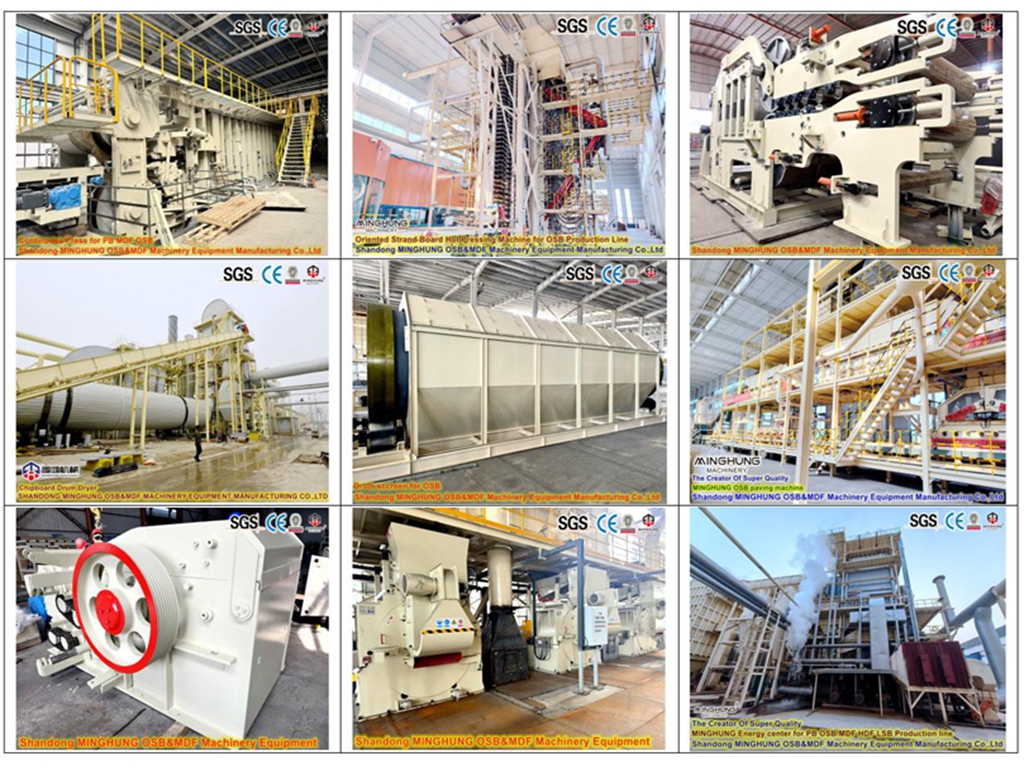


We regularly participate in international industry exhibitions based on the company's business development and customer needs. On one hand, this helps us showcase our company's strength and expand new customers. On the other hand, we visit existing customers for follow-up visits, thereby enhancing the bond between them.