|
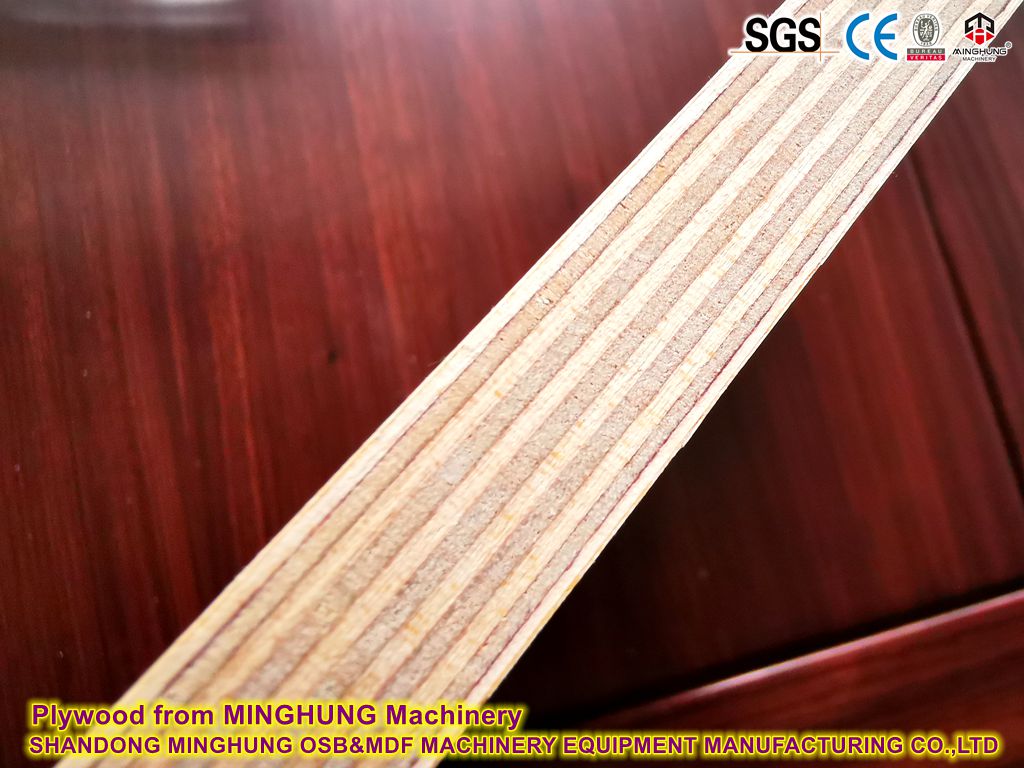
Overview of Plywood

1. Definition and Structure
Plywood is an engineered wood panel made by bonding multiple thin wood veneers (called plies or rotary-cut veneers) with adjacent layers arranged perpendicular to each other’s grain direction, followed by gluing, layup, and hot-pressing. It typically has an odd number of layers (e.g., 3-ply, 5-ply, 7-ply, or more) to ensure structural symmetry and balance, preventing warping.
2. Key Characteristics
High Strength and Stability: The cross-laminated structure provides uniform strength in all directions and excellent bending/tensile resistance.
Size Flexibility: Can be produced in large formats (common size 1220×2440mm) with a wide thickness range (3mm to over 30mm).
High Material Utilization: Suitable for fast-growing timber, small-diameter logs, and wood processing residues.
Strong Decorative Potential: Surface can use high-quality precious wood veneers for dyeing, parquetry, and artistic treatments.
Controllable Environmental Impact: Formaldehyde emissions can be controlled by using eco-friendly adhesives (e.g., E0/E1 grade).
3. Main Classifications
By Use: General-purpose plywood, decorative plywood, special plywood (e.g., marine grade, concrete formwork).
By Water Resistance: Type I (weather-resistant), Type II (water-resistant), Type III (moisture-resistant), Type IV (non-moisture-resistant).
By Surface Treatment: Sanded, scraped, overlaid (with decorative paper, wood veneer, plastic film).
By Wood Species: Hardwood plywood (beech, oak, etc.), Softwood plywood (pine, fir, etc.).
|
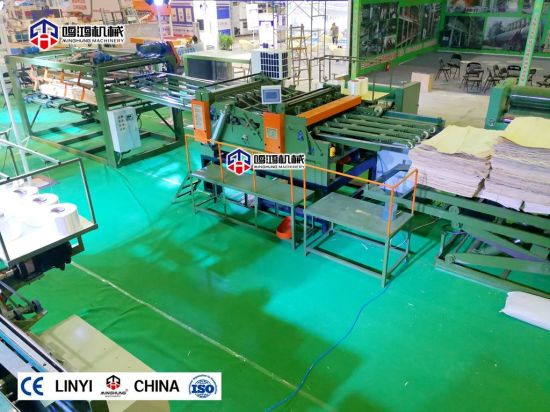
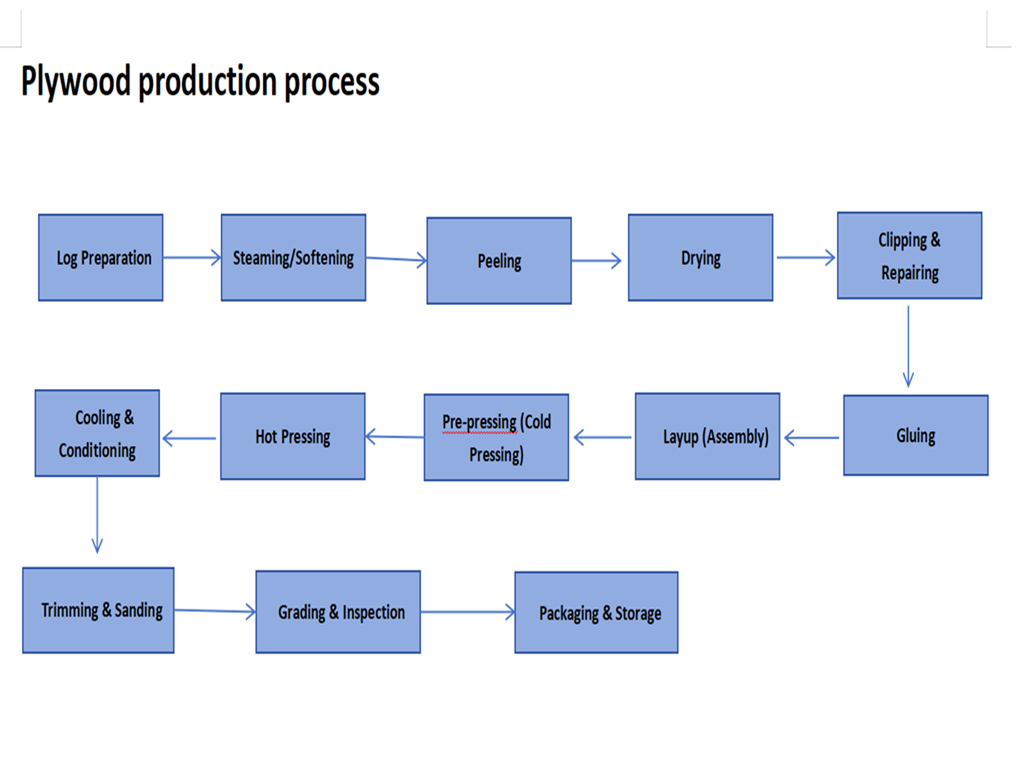
Complete Plywood Production Line Process
Stage 1: Raw Material Preparation
1. Log Processing: Procurement inspection → cross-cutting (to length) → debarking → hydro-thermal treatment (steaming/softening).
2. Veneer Peeling: Lathe peeler rotates logs to produce continuous ribbon veneer (thickness 0.3-4mm).
3. Veneer Processing: Clipping (to width) → drying (moisture content 8-12%) → repair (filling splits/knot holes).
Stage 2: Gluing and Layup
1. Gluing Operation: Veneers are evenly coated with adhesive by glue spreader (roller/curtain coating).
Common adhesives: Urea-formaldehyde (UF), Phenol-formaldehyde (PF), Melamine-urea-formaldehyde (MUF).
2. Layup and Aging: Manual or automatic layup according to preset structure (symmetry principle), followed by short aging for adhesive penetration.
Stage 3: Hot Pressing
1. Pre-pressing: Cold pressing for initial shaping to prevent panel shifting.
2. Hot Pressing: Multi-opening hot press (temperature 110-150°C, pressure 1.0-2.0MPa, time adjusted by thickness).
Key functions: Adhesive curing, moisture evaporation, panel densification.
3. Cooling and Conditioning: Panel cooling after pressing, stacking to balance internal stress (24-48 hours).
Stage 4: Post-processing
1. Trimming: Panel edges trimmed to standard dimensions by cross-cut and rip saws.
2. Sanding: Double-sided thickness calibrating sander (as mentioned by user) performs fine sanding, ensuring thickness tolerance ±0.1mm.
3. Grading and Inspection: Graded by appearance and physical properties according to national standards (e.g., GB/T 9846).
4. Packaging and Storage: Labeling, moisture-proof wrapping, palletizing.
|
Core Equipment in Production Line
Equipment Name | Main Function | Key Technical Parameters |
Veneer Lathe | Peels logs into continuous veneer | Maximum peel length, precision, automation level |
Veneer Dryer | Reduces veneer moisture content | Drying method (roller/mesh belt), energy consumption, uniformity |
Glue Spreader | Applies adhesive evenly on veneers | Glue spread control accuracy (±5g/㎡) |
Layup Line | Automated veneer stacking and patching | Automation level, production speed (sheets/hour) |
Hot Press | Cures panels under heat and pressure | Number of openings, pressure, temperature control accuracy |
Sanding Line | Thickness calibration and surface finishing | Sanding allowance, surface roughness, dust removal efficiency |
Trimming Saw | Cuts panels to final dimensions | Cutting accuracy, automated positioning |

veneer peeling machine

veneer drying machine

sanding machine

trimming saw machine

glue spreader

hot press
|
Double-Sided Thickness Calibrating Sander
The Double-Sided Thickness Calibrating Sander is a core finishing machine in the post-production process of engineered wood panels such as plywood and fiberboard. Its primary function is to simultaneously sand and calibrate the thickness of both the top and bottom surfaces of a panel in a single pass.
Compared to traditional single-sided sanders or machines requiring panel flipping, its key features and advantages are:
1. High-Efficiency Single-Pass Processing: Panels are finished on both sides in one pass, eliminating the need for flipping or a second feed-through, which dramatically increases production efficiency.
2. Precise Thickness Control: Through accurate feed systems and pressure control, it sands panels down to a preset target thickness, ensuring exceptional thickness uniformity across the entire sheet, with tolerances as tight as ±0.1mm or less.
3. Superior Surface Quality: Equipped with multiple sanding heads (e.g., for coarse and fine sanding), it removes surface defects and pre-cured layers, delivering a smooth, consistent finish. This creates the perfect substrate for subsequent processes like laminating or painting.
4. High Automation: It typically integrates automatic feeding, thickness monitoring, and dust extraction systems, making it an essential component of modern, automated, and intelligent panel production lines.
In short, it is an indispensable machine for guaranteeing the final dimensional accuracy and surface quality of engineered wood panels.
|
Company Profile
We are Shandong MINGHUNG Wood Based Panel Machinery Co.,Ltd China factory and manufacturer of full sets of Plywood machinery and Veneer machinery. With many years production experience, advanced production technology,experienced workers and professional engineers, we can offer you the suitable, good and strong machinery for you.






























































