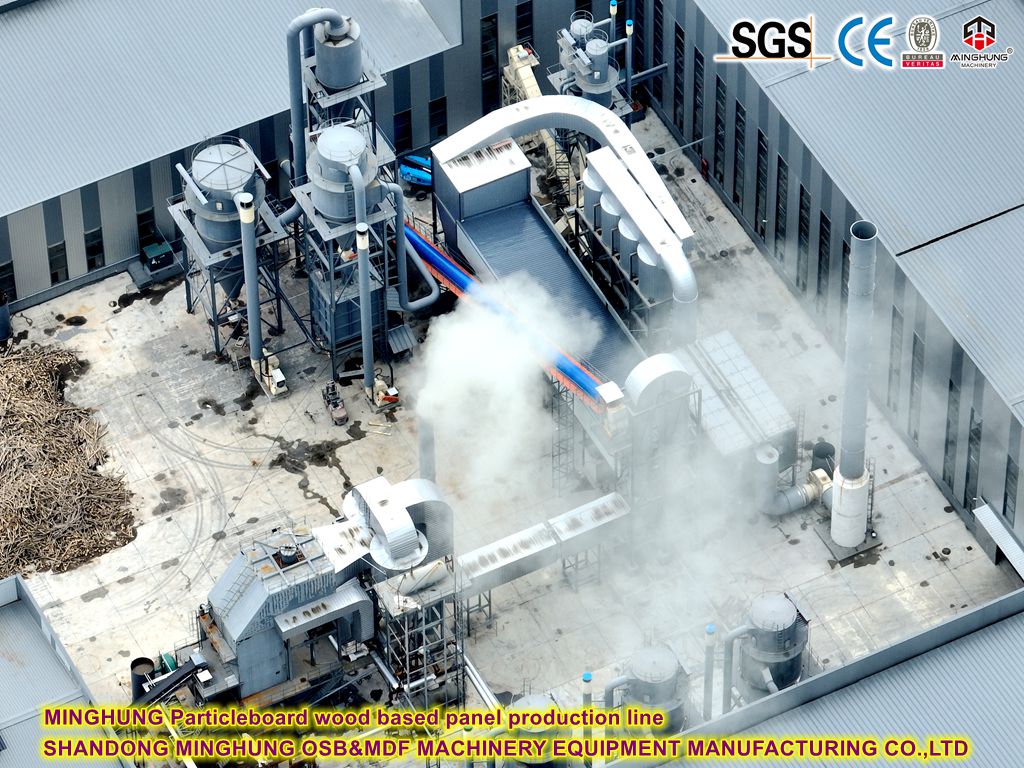
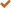This production process is a highly automated and continuous industrial operation designed to efficiently convert pine raw material into high-quality particleboard. The entire process can be divided into the following core stages:
Stage 1: Raw Material Preparation
1. Debarking: Pine logs are first processed through a drum debarker to remove bark. Bark can affect board quality and appearance and is typically collected to be used as biomass fuel for the plant's energy system.
2. Chipping: Debarked logs are fed into a large drum chipper to be processed into uniform, industry-standard wood chips.
3. Flaking and Crushing: The wood chips are further processed:
Flaking: Flakers convert the chips into flat flakes.
Screening and Crushing: The flakes are screened. Oversized flakes are sent to crushers to be reduced, obtaining flakes of different sizes. Typically, finer flakes are used for the board surfaces, while coarser flakes are used for the core, ensuring a smooth surface and a strong internal structure.
Stage 2: Drying and Screening
4. Drying: Wet flakes are passed through a rotary drum dryer, using hot air (often from a biomass boiler burning wood waste) to precisely reduce their moisture content from about 40-60% to the required 2-4% for processing. Precise moisture control is critical for subsequent blending and pressing.
5. Screening: The dried flakes are precisely sorted by a multi-deck vibrating screen into surface-grade fine flakes, core-layer coarse flakes, and oversize flakes that need to be recrushed.
Stage 3: Blending and Forming
6. Blending: The sorted flakes are conveyed separately to large ring blenders.
Core-layer flakes are mixed with the main adhesive (e.g., Urea-Formaldehyde UF or MDI).
Surface-layer flakes are mixed with a higher proportion of adhesive and additives (e.g., wax emulsion for waterproofing).
This process ensures each flake is uniformly coated.
7. Forming: The blended flakes are distributed by an advanced forming station. The former creates a "core-surface" structure, first laying down the core-layer coarse flakes, then evenly distributing the fine flakes on the top and bottom surfaces to form a continuous mat with a symmetrical structure and uniform density distribution.
Stage 4: Pre-Pressing and Pressing
8. Pre-Pressing: The loose mat is initially compressed by a pre-press. This compacts the mat, removes air, and adds strength for easier transfer into the main press.
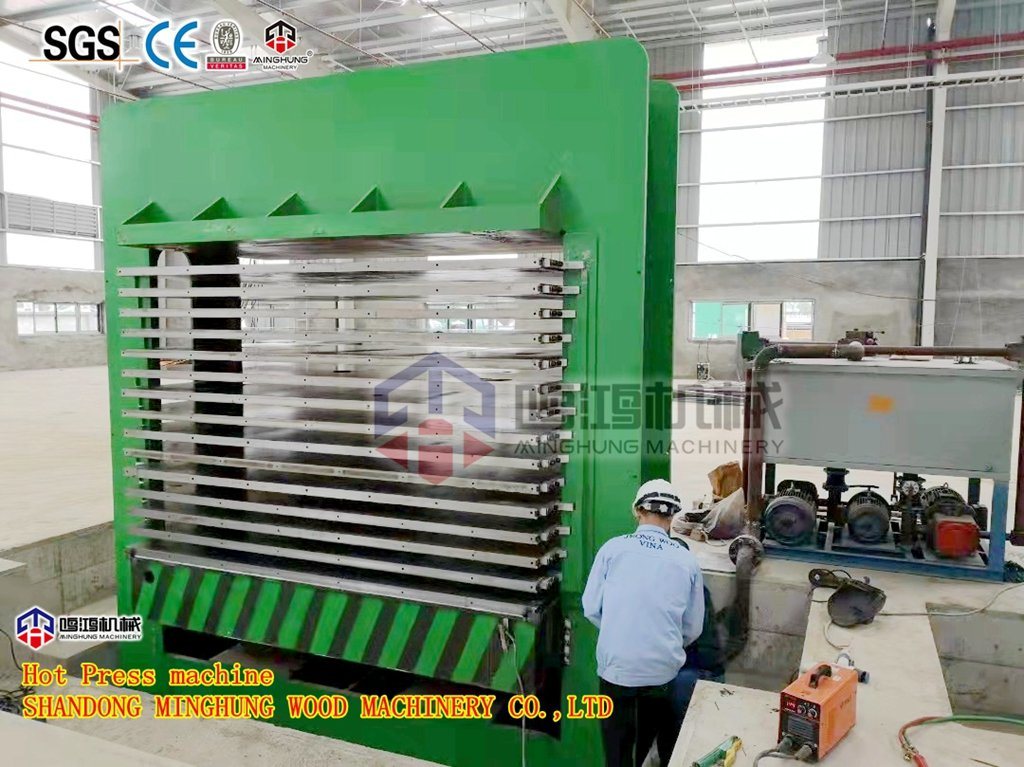
9. Pressing: This is the core step of the process. The mat enters a continuous press (Continuous Press). Under high temperature (200-220°C) and pressure, the mat continuously passes through the heated platens. The adhesive cures rapidly within seconds, bonding the loose flakes into a solid board. Continuous press technology ensures precise thickness, uniform density, a smooth surface, and extremely high production efficiency.
Stage 5: Finishing and Storage
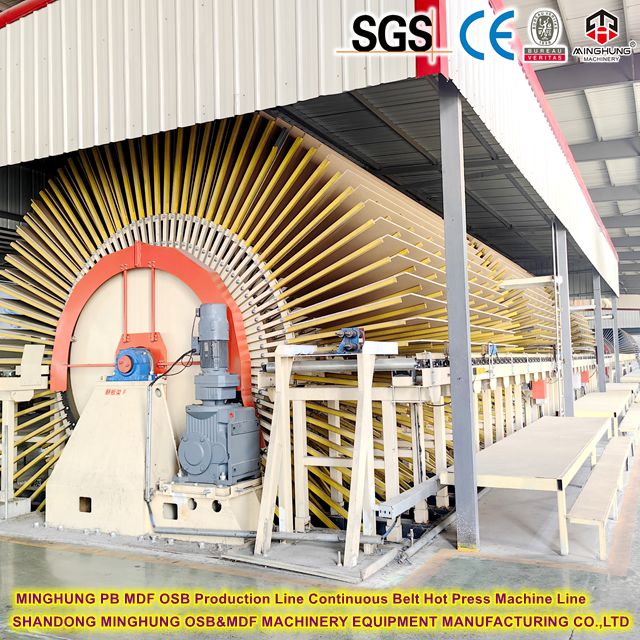
10. Cooling: The hot boards exiting the press are fragile and are immediately sent to a cooling star for forced cooling. This stabilizes internal stresses and evaporates residual moisture.
11. Sawing: The cooled continuous board is cut to standard sizes (e.g., 1220mm x 2440mm) or custom dimensions by high-speed cross-cut and trim saws.
12. Sanding: The boards are processed through a precision calibrating sander to sand the top and bottom surfaces. This eliminates thickness variation and the pre-cured layer, resulting in a smooth, flat finished product with precise thickness.
13. Inspection and Packaging: Boards undergo final quality inspection (checking thickness, density, appearance, etc.). Approved products are automatically stacked and packaged.
14. Storage: Packaged finished products are stored in the warehouse, awaiting shipment.